
test

2 End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture

goal 3

goal 4

goal 5

goal 6

goal 7

goal 8

goal 9

goal 10

goal 11

goal 12

goal 13

goal 14

goal 15

Goal 16
16.3: Promote the rules of law and the national and international levels and ensure equal access to justice for all.
16.5: Substantially reduce corruption and bribery in all their forms
16.7 Ensure responsive, inclusive, participatory and representative decision-making at all levels
16.b: Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development

Goal 17
WATER MANAGEMENT
Long term target: In 2032 reduce 15% of water consumption per revenue from base year (2021)
The attention to effective water management remains to be an importance influence amongst businesses decision-making throughout 2024, as water resources remains to be one of the world’s most valuable resources, consumed and used by consumers and businesses alike throughout the value chain in the production of products and services. In 2024, climate change is continually affecting water availability worldwide, leading to more frequent and severe droughts, floods, and water scarcity in certain regions. This has heightened the urgency of effective water management and conservation to cope with changing climate patterns. Addressing water challenges requires a collective effort from governments, businesses, communities, and individuals to ensure the responsible use, protection, and equitable distribution of this precious resource.
BJC sincerely acknowledge the severity and urgency to effective water management, since water is a fundamental resource to sustain life, and essential to business operations. A lack of effective water management not only pose physical risks to companies, affecting operations and value chains, but also reputational risks, as media and publics become more aware of some company’s contribution to unsustainable water consumption. Reputational risk is further intensified for companies located in water-stress areas, since companies risk imposing the human rights to water and sanitation of surrounding communities, especially during 2021-2024, as water is an essential aspect to safeguard employees and surrounding societies against the spread of the pandemic.
The prioritization of effective water management remains in place, despite the appearance that water scarcity is not a material issue in Thailand. Yet, in reality, water related issues such as flooding and droughts are important considerations and are actively integrated in strategic planning to ensure sufficient access to clean water resources for consumption. As such, water remains to be a critical challenge to Thailand and BJC to develop long-term plans to achieve efficient and sustainable water utilization and consumption. For these reasons, BJC continued to identify, developed and implement diverse water management programs to assess BJC’s exposure to water related risks, whilst identifying potential opportunities, in order to actively manage and optimized water resource utility throughout the value chain.
Water Indicators
BJC remains committed to effective water utilization, aiming to efficiently withdrawal, consume and discharge water resources in a responsible manner, in accordance with applicable environmental standards, laws, and regulations, in addition to the corporate-wide environmental policy.
| Water Indicator (Million cubic meters) | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
| A. Total Water Withdrawal | 8.54 | 8.51 | 9.86 | 10.21 |
| i. Municipal Water Supplies (or from other water utilities) | 8.40 | 8.22 | 9.60 | 9.90 |
| ii. Fresh Surface Water (lakes, rivers, etc.) | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| iii. Fresh Groundwater | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.21 |
| iv. Produced Water | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| B. Total Direct Water Withdrawal (from Water Stress Area) | 2.50 | 1.87 | 2.38 | 7.34 |
| Water Discharge | ||||
| C. Total Water Discharge | 4.70 | 4.35 | 6.38 | 7.46 |
| i. Water Discharge to Surface Water | 0.44 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| ii. Water Discharge to Ground Water | 3.02 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 |
| iii. Water Discharge to Third-Party Water | 1.24 | 4.30 | 6.32 | 7.37 |
| D. Total Direct Water Discharge (to area with water stress ) | 1.51 | 1.07 | 1.42 | 4.99 |
| Water Consumption | ||||
| E. Total Water Consumption | 3.84 | 4.16 | 3.48 | 2.75 |
Remark : Data verified by third party.
|
Water Consumption (Million cubic meters) |
2021 |
2022 |
2023 |
2024 |
Target for 2024 |
| A. Water Withdrawal (Excluding saltwater) |
8.54 |
8.51 |
9.86 |
10.21 |
|
| B. Water Discharge (Excluding saltwater) |
4.70 |
4.35 |
6.38 |
7.46 |
|
|
Total Net Fresh Water Consumption (A-B) |
3.84 |
4.16 |
3.48 |
2.75 |
3.40 |
| Data Coverage (as % of denominator) |
89.98 |
91.37 |
91.42 |
91.81 |
Water Related Risk Assessment and Results
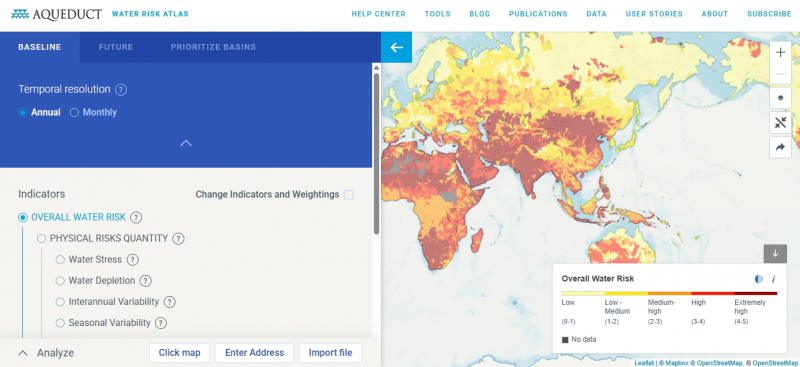
To assess water-related risks and foster awareness and effective management of water-related risk throughout all operations, BJC has integrated water-related risk considerations such as flooding and water stress into the corporate-wide strategy, driving BJC to actively identify potential water-related risks in different operating locations. Assessments are conducted through 2 primary approaches. For operations with production and manufacturing activities, water-related risks are assessed under compliance with international standards such as ISO 14001:2015, while other operations such as headquarter and office-based activities are assessed by the internal audit department, in accordance with internal standards, based on ISO 14001 criteria. To accurately identify operations located in water stress areas, BJC employs the open source data tool Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas, developed by World Resources Institute (WRI) to identify areas of water stress where suppliers operate, and the areas are mapped by inputting BJC operation site locations and supplier locations into the tool. Assessment results have enabled BJC to develop a comprehensive Business Continuity Plans (BCP) which emphasis on the efficient management and actions during flood and drought situation, to ensure business resilience during different situations. Furthermore, assessment results permit BJC to determine the overall impacts water-related risks imposed on operations.
To minimize risks related to the quantity and quality of water, BJC conducts on-site Factory Audit annually, on all critical tier-1 suppliers, to evaluate suppliers’ wastewater treatment system along with the water quality discharged to minimize risks related to the quantity and quality of water. In the case that water quality does not meet requirements, a corrective action plan must be defined and then be completed. Furthermore, BJC continued to implement various water management programs with our supplier to assess BJC’s exposure to water related risks, whilst identifying potential opportunities, in order to actively manage and optimize water resource utility throughout the value chain. From the BJC's perspective, water and wastewater management is one of the priority topics we assess through the new suppliers' selection process.
(I) Assess and Interpret & Prioritize
BJC Group identify the most material impacts on natural resources by referring to Corporate Environmental Policy which mentioned about protected areas, including the World Heritage areas in accordance with the criteria of UNESCO, and protected areas according to The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) category 1-4. BJC Group use these areas as the target protected areas for business units to verify if BJC’s and critical suppliers’ operational activities are close by.
BJC also use Aqueduct™ tools to identify and evaluate current water risks in all Thailand’s provinces (baseline water stress level). The tools belong to World Resources Institute (WRI), which can map water risks such as floods, droughts, and stress, using open-source, peer reviewed data.
In 2024, BJC assessed water risk at sourcing locations of key agricultural commodities such as Palm oil, Sugar and Cacao which is the main raw materials in the production process through the analysis from the Aqueduct Water Risk Atla tool. For palm oil, 7 sourcing provinces have been assessed, which included Chumphon, Krabi, Surat Thani, Chon Buri, Prachuap Khiri Khan and Trat. For sugar, 9 sourcing provinces have been assessed, which included Chaiyaphum, Lopburi, Nakhon Sawan, Phetchabun, Sukhothai, Kalasin, Khon Kaen, Uttaradit and Loei. For Cacao, 3 sourcing countries have been assessed, which included Netherland, Malaysia and Singapore.
(II) Measure & Set
In 2024, BJC utilizes the ‘Aqueduct’ tool developed by the World Resource Institute (WRI) to assess own and supplier’s operation locations to determine if they are operating in water stress areas. The assessment demonstrates that the majority of our critical tier-1 suppliers (84%) are located in the high water risk area, while 5% of our critical tier-1 suppliers are located in the low-medium water risk area, 3% are located in the medium-high water risk area, 4% of our critical tier-1 suppliers in the extremely high water risk area, and 4% are located in the low water risk area. We consider critical suppliers located in the high water risk area to have water-related risks and prepare mitigation plans.
(III) Mitigation Plan
Berli Jucker Foods Co., Ltd. (BJF)
Berli Jucker Foods Co., Ltd. (BJF)’s own operation takes place at 2 operational sites, located in the industrial parks of Samut Prakan province and Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya province. Regarding to the current water risks in Thailand, Samut Prakan province has a extremely high water stress level and Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya province has a high-water stress level.
Mitigation Plan
BJF’s operational site in Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya province is located in Rojana Industrial Park, which is a high-quality industrial park guaranteed by the international standard ISO9001, and BJF’s operational site in Samut Prakan province is guaranteed by the international standard ISO14001. Both operational sites provide the international standard infrastructure network to conserve water, including high-quality industrial water, sanitary sewers, and high-technology wastewater treatment plants. Not only the high-quality industrial park that mitigates the water risks.
BJF itself also gives special attention to water management practice by implementing Water Recycling Management in order to reduce water consumption and preserve the water resources available in the area. BJF’s primary water consumption dominates at the potato chip processing, where water is used in 3 stages of the potato chip processing: peeling, slicing, and washing potatoes. Moreover, to minimize wastewater, the water from the washing process is filtered by a filtering machine and recycled as a supply to potato chip processing once again. This management approach has resulted in a reduction of wastewater by 15% annually.
Berli Jucker Foods Co., Ltd. (BJF) - Critical suppliers
- There are 5 critical suppliers supplying potatoes to BJF, 1 of them is located in a high-water stress level province and 3 of them are located in extremely high-water stress level provinces.
- For palm oil, 7 sourcing provinces have been assessed and 1 is located in extremely high-water stress level province.
- For sugar, 4 sourcing provinces have been assesses and all located in extremely high-water stress level province.
Mitigation Plan
BJF has given all suppliers a strict operational guideline to conserve water which have been well agreed upon and followed by the suppliers. The guideline includes the following instructions;
- Suppliers must cultivate potatoes on farmland with reliable water sources, such as dams or irrigation systems.
- Farmers should receive thorough training on efficient water use in potato cultivation to prevent overwatering.
- Farmers' practices must be advised and closely controlled to use water cost-effectively. Farmers who have already utilized water in their own plots will release the water to the next farmer until the last plot, and drain it back to natural water sources for cost-effective use and for conserving the water resources.
- Farmers should be encouraged to construct natural or wastewater reservoirs within their plantations to minimize negative impacts on local water resources.
Berli Jucker Cellox Co., Ltd. (CPC) - Critical suppliers
Berli Jucker Cellox Co., Ltd. (CPC) has 8 critical suppliers. That the operational sites of critical suppliers are located in Prachin Buri province and China, which have an extremely high-water stress level, Bangkok province and Samut Prakan province, which have a high-water stress level, Singapore has a low water stress level and Hongkong has a medium-high water stress level.
Mitigation Plan
The supplier strictly abides by the laws, rules and regulations. According to their policy, they are committed to operating better standards which are friendly to the environment, society and community. The supplier also conducts the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) and Health Impact Assessment (HIA) to ensure that the performance has met the accepted-standard. Moreover, to mitigate water risks, the supplier has been conducting the following environmental measures;
- Supplier consumes water from its own reservoir and manages raw water and water for industrial use by pumping overflowing water around the reservoir and raw water from the nearby river into the reservoir, pumping the stored raw water into the water treatment plants.
- Supplier treats waste water from electricity generation better than the standards. The treated waste-water is used to water the trees and garden around the power plants.
Thai Beverage Can Co., Ltd. (TBC)
Thai Beverage Can Co., Ltd. (TBC) has an operational site located in Saraburi, which is a extremely high-water stress level province. The operational site is located in WHA Saraburi Industrial Land.
Mitigation Plan
WHA Saraburi Industrial Land provides 785 million cubic meters of ample water supply from Pasak Cholasith Dam, and wastewater treatment to every factory in its area. Water is provided through WHA Utilities and Power Public Company Limited (WHAUP), Thailand’s largest private provider of industrial water production and distribution. WHAUP ensures that the used water is treated in accordance with applicable standards imposed by the Ministry of Industry before being discharged into the center wastewater treatment of each industrial estate. The treated wastewater can be discharged into natural sources of water or be recycled into the production process, aiming to conserve water in the area. Moreover, in 2020 WHA Saraburi Industrial Land has built reservoir reserves to support the drought crisis, which has increased by about 300,000 m3.
Thai Malaya Glass Co., Ltd. (TMG)
Similar to TBC, Thai Malaya Glass Co., Ltd. (TMG) has an operational site located in Saraburi, which is a extremely high-water stress level province. The operational site is located in WHA Saraburi Industrial Land.
Mitigation Plan
WHA Saraburi Industrial Land provides 785 million cubic meters of ample water supply from Pasak Cholasith Dam, and wastewater treatment to every factory in its area. WHA has built extra reservoir reserves to support the drought crisis, which has increased by about 300,000 m3. TMG has also implemented a plan to mitigate the water risks and the plan includes the following items;
- TMG has built artesian wells, which can supply enough water for daily use. The artesian wells are reserve wells, which will be utilized only when WHA Saraburi Industrial Land fail to supply water.
- TMG is already working on using ozone in coolant treatment in the cooling tower.
- TMG utilizes water recycling instead of freshwater to wash glass cullet, help reduce dust, and retain moisture, and it also prevents the formation of foam caused by the reaction of organic substances during the melting process.
(IV) Track
To minimize risks related to stakeholder conflict, BJC continues to communicate with all stakeholders and regularly monitors our supplier’s grievance records and logs, which a part of the factory audit, and routinely engages with stakeholders through various channels, to ensure that the potential conflicts with stakeholders (e.g., local communities) are mitigated. However, suppose risk related to stakeholder conflict is addressed. In that case, the Procurement Department and the Quality Assurance Department will work intimately with our critical tier-1 suppliers to ensure the risk will be mitigated cohesively. If conflicts between suppliers in water-stressed areas and stakeholders occur, we will initiate appropriate measures to solve those conflicts that may affect the company's business operations and maintain relationship with relevant stakeholder.
All business units and their critical suppliers monitor and validate their mitigation plans and actions annually, with a disclosure through BJC Annual Sustainability Report or the company website. The mitigation plans and actions are reviewed for their accuracy, efficiency and effectiveness, as well as for the next year planning. For the operational sites located in the industrial estates, the industrial estates also have their water risks mitigation plans reviewed and updated regularly. This is to maintain their quality of utilities service excellence for all sites operating in their areas.
BJC assigned the Legal Department to regularly monitor regulatory changes related to water use and pricing structures to minimize potential risks.If any changes could affect the business or suppliers, the Legal Department promptly informs the relevant functions, including Procurement and Quality Assurance.These departments then work closely with critical tier‑1 suppliers to assess impacts and determine appropriate mitigation measures.This proactive coordination ensures suppliers remain compliant and operational risks are minimized.

Wastewater Management
BJC consumes water from various sources, depending on the accessibility and availability of water resources in each location. These water sources include municipal water, which is the primary source and is underground, consumed at factories and some upcountry Big C stores. Recognizing the impacts of effluent discharge from operations such as factories on surrounding ecosystem and communities, BJC is committed to continuously monitor water quality to ensure that all water discharged from operations are treated in accordance with national best standards. To uphold this commitment, BJC has developed an internal wastewater treatment procedures which provide a clear guideline to wastewater treatment prior to discharge in accordance with relevant natural resource industrial regulation best-practices. BJC emphasizes on the compliance with the most stringent industrial best-practice regulations such as the Ministry of Industry’s water discharge regulations. This includes periodically reporting and monitoring water quality, and quality of effluent treated by the internal wastewater treatment systems. These are conducted by external inspectors certified by the Department of Industrial Work. To accurately implement relevant standards at each facility, an environmental supervisor are trained and certified in accordance with the Ministry of Industry’s requirements and the Thai Environment Institute to monitor the properties of treated wastewater and to ensure that it is safe to be discharged into municipal wastewater treatment systems for additional treatment, or to be reused within the facility such as cleaning and watering green spaces.
Furthermore,ฺ BJC engages with local communities on a regular basis to listen and address any concerns they may have. Grievance channels including websites, telephone number are available at all BJC’s facilities. Additionally, communities can directly raise their concerns to human resource department or environmental committee at each facility, as well as government authorities. The department holds the responsibility to record and mediate concerns raised. BJC endeavors to protect and preserve this natural resource for future generations.
Highlight Activities
SUSTAINABLE WATER MANAGEMENT AT TGI
To prepare for the increasingly unpredictable weather and rainfall pattern, in addition to the drought warning forecasted by local government, Thai Glass Industries PLC (TGI) implemented projects to improve internal water consumption and discharge to minimize water consumption and increase water efficiency. Projects include upgrading water systems through improved monitoring equipment such as piping systems, water pumps, and sludge treatment pond, reducing the facility dependency on municipal water sources.
To prepare for the increasingly unpredictable weather and rainfall pattern, in addition to the drought warning forecasted by local government, Thai Glass Industries PLC (TGI) implemented projects to improve internal water consumption and discharge to minimize water consumption and increase water efficiency. Projects include upgrading water systems through improved monitoring equipment such as piping systems, water pumps, and sludge treatment pond, reducing the facility dependency on municipal water sources.
In 2020, to accommodate for the increased circulation of reused treated wastewater, TGI increased the storage capacity of on-site wastewater storage tanks enabling the facility to increase utilization of wastewater for various projects. The upgrade results in an increase capacity of on-site wastewater storage from 1,526 m3 in 2019 to 6,432 m3 in 2020. Beyond increasing water storage capacity, TGI also conduct repairs of furnace under the BP2 furnace major repair project, to increase furnace efficiency, which in turn, reduced water consumption. The repair resulted in 1,541 m3 per month, equivalent to 5,912 cubic meter annually.
Prior to reusing wastewater throughout the facility for productive purposes, all wastewaters are treated in accordance with applicable safety standards including the Ministry of Industry sewage control standards for factories 2017. The quality of treated wastewater are monitored twice a month, ensuring water quality safety. The improved water storage system supplies reuse water to utility machines throughout the facility, enabling TGI to reduce an estimate of 4,000 cubic meter per year.
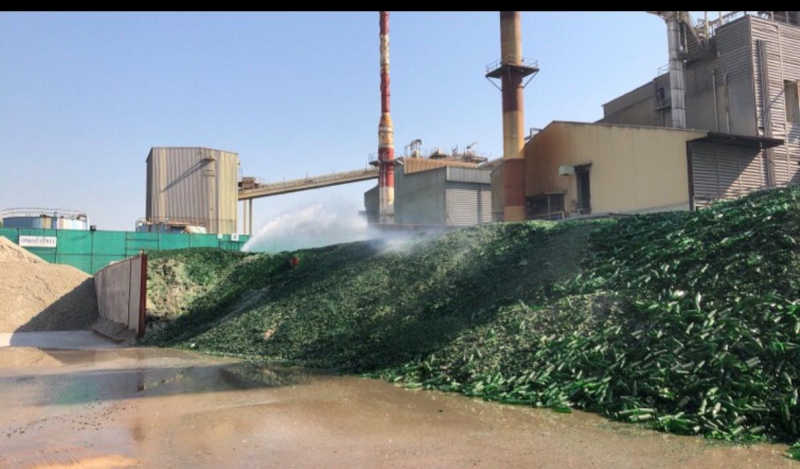

Finally, to control the emissions of cullet dusts to surrounding communities, TGI installs water sprays over the cullet reserves to periodically spray treated waste over the cullet to prevent dusts from flowing to surrounding communities. This reduces the consumption of municipal water by 2,700 cubic meter per year, equivalent to 45,900 Baht a year.