
test

2 End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture

goal 3

goal 4

goal 5

goal 6

goal 7

goal 8

goal 9

goal 10

goal 11

goal 12

goal 13

goal 14

goal 15

Goal 16
16.3: Promote the rules of law and the national and international levels and ensure equal access to justice for all.
16.5: Substantially reduce corruption and bribery in all their forms
16.7 Ensure responsive, inclusive, participatory and representative decision-making at all levels
16.b: Promote and enforce non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development

Goal 17
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
Data and Cybersecurity Privacy Protection Strategy
Over the past few years, businesses have seen a significant rise in the number and complexity of cybersecurity threats, and this trend is expected to continue in the years to come. The threat landscape is becoming more challenging, as new technologies and trends create new opportunities for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities in corporate systems. The cybersecurity and data privacy threats that businesses face in 2022 were complex and evolving. Phishing attacks, insider threats, cloud security, and the shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals were just a few of the trends that businesses need to be aware of.
Data and cybersecurity privacy protection have both negative and positive impacts on the economy, environment, and people. The negative impacts include the risk of financial losses due to cyber-attacks, which can result in significant economic damage to businesses and the wider economy. Additionally, the harm to customers' privacy rights can have serious implications for human rights and consumer trust in organizations. Moreover, network damage or disruption can cause data loss and downtime, which can be costly and disruptive to business operations and overall productivity. On the positive side, stronger security measures can help protect against cyber threats and safeguard sensitive data, leading to increased consumer confidence and trust. Convenient and user-friendly security measures can also encourage wider adoption of digital technologies, which can lead to increased economic growth and innovation.
BJC realized that to create awareness and preparation by protecting its assets and data, it must prioritize cybersecurity and take proactive measures above and beyond to balance the value of new technology and the cyber risk that may come with it. Moreover, the company must invest in training and development programs to help grow its own cybersecurity talents and ensure they have the necessary skills to protect the digital assets.

Data and Cybersecurity Privacy Protection Management Approach
BJC has always been committed to upholding comprehensive and robust Cybersecurity and Data Privacy measures. This is demonstrated through the corporate-wide Information and Cybersecurity Policy, which is available in the company website and can be accessed by all employees, providing a complete guideline for all business operations under BJC and its subsidiaries. The policy instructs employees on the appropriate practices to ensure data security and promptly manage all cybersecurity attacks. The policy was developed and overseen by the Centralized Management Information System under the guidance of the Information Technology Management Structure, which is responsible for the management and prevention of all cyber security, and cyberattack related topics, including revision of the information and cybersecurity policy, strategies Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP), Vulnerability Assessment (VA) oversight, and penetration/stress tests.
BJC had taken steps above and beyond to enhance its cybersecurity and data privacy measures in 2022 due to the increasingly severe global threat of cyberattacks. The company viewed information security as a critical aspect and included it on the agendas of key meetings; the monthly Management Board meetings, Risk Management Committee meetings, and annual Sustainable Development Committee meetings.
BJC prioritizes information security, including cybersecurity and data privacy, and has established various measures and committees to ensure that best practices are in place and continuously reviewed to stay ahead of evolving risks.
Information Technology Management Structure

Information Technology Management Structure
Mr.Aswin Techchakareonvikul the executive vice chairman and a member of the board member is experience in information technology through jointly invested in the big data development through the C smart Solution Co., Mr. Aswin participates in CSS’s monthly business review, which examine financial & non-financial performance. For non-financial performance the main agenda is related to key operations of CSS, including information management and information security etc., ensuring that business meets corporate objectives. In addition, Mr. Aswin is also involved in assessing projects and other innovations/initiatives related to information technology, prior to its implementation, thus this evidence his experience related to big data and IT management. Today he is the lead of the BJC cybersecuriyy committee, responsible for overseeing all matters related to cybersecurity.
The management structure is also accountable to oversee cybersecurity management and foster a corporate-wide cybersecurity culture, which has been achieved through raising awareness amongst all employees by online learning courses and the newsletters that aim to reduce the risks of cyberattacks. BJC regards information security as one of the most critical aspects of the organization and includes it on the agendas of Management Board meeting held on a monthly basis and Risk Management Committee meeting held on a quarterly basis, The Management Board acknowledges any a process in place to prevent information system interruptions and cyberattacks within a timely manner, and actions for preventing recurrence of situation. The Company has an Information Technology Committee that defines, evaluates and reviews strategies, scope, and operations in information technology structure. The committee has a monthly meeting and it consists of MIS Technology department personnel and other departments involved in information technology structure. These set overall operational guidelines, including best practices regarding personal information security, as well as training and education for employees and stakeholders. Moreover, there is Data Protection Officer or DPO that educates and trains employees involved in data processing, ensures compliance and proactively addresses potential issues. The DPO is also a contact point between the company and Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) regulator, monitoring the effectiveness and the impact of data protection efforts.
Throughout 2022, the Management Board maintain its recognition of the critical importance of cybersecurity and has taken concrete steps to prioritize it within the organization, including the establishment of the Cybersecurity Committee. They have approved an Information Technology Management Structure that is led by the Chief Executive Officer and President. This team continuously invests in big data development through the C Smart Solution Co., Ltd (CSS), a dataanalytics company, and oversees the overall IT management systems with the assistance of the Executive Vice President of the IT department, who serves as the Chief Information Officer (CIO). This structure integrates cybersecurity throughoutthe entire value chain through a corporate-wide information technology strategy, developed with principles that uphold the Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA) of all business goals. BJC's internal information technology is managed by the Management Information System department, which provides assistance related to information technologies, including the development of a robust cybersecurity infrastructure and cybersecurity guidelines. The Information Technology Security Department is responsible for managing all cybersecurity incidents, ensuring that all digital risks management and data protection initiatives align with internal guidelines and all applicable external laws, regulations, and standards, which are closely monitored through a rigorous process. These efforts demonstrate BJC's unwavering commitment to information security and cybersecurity. In addition, BJC realized the speed at which emergent technologies are used frequently outraces the company’s capacity to develop safeguard, so the company must step beyond simple regulatory compliance in order to be cyber resilient business.
BJC places great emphasis on information security and has undergone an audit to certify its Information Security Management System (ISMS) in accordance with international standard ISO 27001. In response to the pandemic and the transition to remote work, the company has also developed additional protocols, policies, and preventive mechanisms to ensure the secure handling of internal information. BJC utilizes a comprehensive Cybersecurity Management Process to identify and eliminate cyber threats, and all employees are encouraged to report any suspicious activity through various channels. All IT risk incidents are reported to the Risk Management Committee on an annual basis, and managed in accordance with internationally recognized standards such as ISMS (ISO 27001) and the Enterprise Risk Management framework (ERM). These efforts demonstrate BJC's strong commitment to information security and their dedication to effectively and promptly managing all cybersecurity risks to prevent any potential operational impacts.
BJC has also implemented Management Information System Division (ISD) to ensure that cybersecurity and infrastructure within BJC are managed properly through a centralized structure. Any Information Technology risk incidents will be reported to Risk Management Committee quarterly to be handled in alignment with Enterprise Risk Management Framework (ERM) and the company policy. The committee is responsible for reporting and receiving advice to ensure that company manages information security and cybersecurity risk effectively and appropriately, in order to prevent and mitigate negative business impacts. Additionally, Information Technology system has been audited to certify Information Security Management System: ISMS (ISO 27001) to ensure that internal information is handled effectively in accordance with international standards, as well as to develop additional protocols, policy and preventive mechanisms during the pandemic.
Moreover, in addition to the BJC Privacy Protection Policy, the company embedded the privacy and personal information risk to the group-wide risk management / compliance management and relevant departments. Risk management framework for risk assessment about personal data protection, including impact assessments has been established to perform assessment by data owner. The company has in place the process to consider the risk regarding personal information and take appropriate measures, determined the operational process related to personal data, and regularly examined it by the Internal Audit department.
Policy and Cybersecurity Test
BJC has implemented BJC’s information and cybersecurity policy and cybersecurity test. The policy focuses on the measures that employees need to follow regarding the use of IT equipment. In addition, cybersecurity tests such as Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP), Penetration test, and Vulnerability Assessment (VA) have been tested at least semi-annually to ensure that its cybersecurity management remains effective and evolves appropriately with BJC. Furthermore, IT infrastructure and information security management systems also have been audited by external auditors in order to criticize accounting procedures and general processes and to develop an action plan for greater productivity. In addition, BJC's suppliers have insurance cover for information security breaches, resulting in BJC being protected against this incident.
Cybersecurity Management Process
BJC places great emphasis on information security and has ungergone an audit to certify its Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) in accordance with applicable international standards, such as the Information Security Management System: ISMS (ISO 27001) to ensure that internal information is handled effectively by international standards. In 2022, 100% of BJC's IT infrastructure and information security management systems has been certified. Additional protocols, policies, and preventive mechanisms have also been developed in response to the pandemic to accommodate the transition in working styles. Cybersecurity Management Process has also been used to eliminate and prevent cyber threats. In the process, all employees are encouraged to report all suspicious cyber activities, which can be reported through various channels including company’s secretary’s email, hotline and direct supervisor. All information technology risks incidents are reported to the Risk Management Committee quarterly to manage in accordance with Enterprise Risk Management framework (ERM), and internationally recognized standards such as ISMS (ISO 27001), ensuring that all information and cybersecurity risks are effectively and promptly managed to prevent operational impacts.
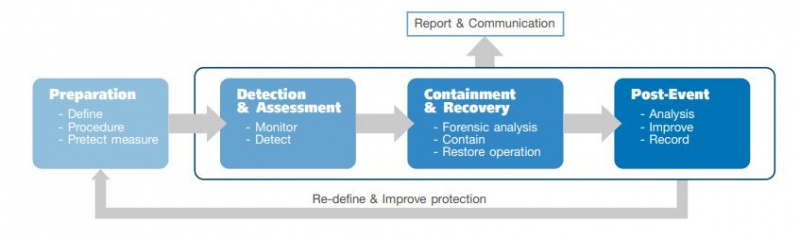
Privacy Protection
BJC places great importance on our customers' personal information protection as we are aware of data privacy and the upcoming PDPA laws in the near future. Therefore, the process has been set up to ensure that BJC has established effective policies and procedures. The Privacy Policy clearly outlines the objective and uses of collected data, which includes behavior analysis, lifestyle and purchasing history to develop a customized marketing campaign that meet customer needs. To protect this personal information, BJC is committed to continuously develop and update policy and documents in accordance with the protection of personal information periodically, or every time the relevant laws are revised, or every time the company’s internal practices are changed or at least once a year. To ensure that personal data protection policies are compliant with applicable laws and regulations. Therefore, BJC has been audited security and data privacy according to the requirements of ISO 27001:2013, which covers personal protection policy compliance. In addition, we also conduct internal audit by internal audit department follow scope of the Bank of Thailand's announcement relating to data security and privacy such as Information security system, Data confidentiality.
About communication, there are three groups of stakeholders in data protection communication as follows;
1. Customers - prepares a consent letter to disclose information to notify customers about the purpose of data collection including other requirements to comply with the PDPA act.
2. Employees - organizes a training course on information security to ensure employees' awareness of information security and how to prevent data leakage.
3. Suppliers - communicates with suppliers regarding data privacy through the supplier code of conduct to comply with BJC's requirements.
In order to rasie awareness on the importance of personal data protection throughout BJC, PDPA Committee meetings have been organized monthly. The meetings aim to ensure that employees are aware of the act and to provide PDPA updates to the executives and related departments.
Customer Privacy Information
As the provisions of the National Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) come into effect on 1st June 2022, BJC has established customer data collection processes by emphasizing on customer data storage, the authorized use of personal data and data protection method to comply with the Protection Act. Currently, BJC has continuously developed the process to inform customers about objective and the use of personal information through privacy notice on company website and consent letter with the following details;
- Nature of information captured from customer information in the request form, contract, letter or other documents, company's website, cookies or applications and telephone system
- Period of data collection
- The purpose of collecting and use of personal data
- Possibility for customers to decide how private data is collected, used, retained and processed e.g. customer data collection, option in-out in consent, availability of opt-out option, request access to data held by the company, request data will be transferred to other service providers, customer request data will be collected and deleted.
- Data protection management by defining authorization and access control for only related parties including
- Organizing training program to raise awareness for employees in accordance with personal data protection act (PDPA), law and regulations. In additional,
- The implementation of customer privacy policy and measure to prevent data leakage
- Contract on personal data protection

To address customers' personal information protection, with regards to the national Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) that would take effect in 2022, BJC has established Personal Data Protection Policy to be applied to BJC and subsidiaries business operations, including suppliers. The policy determines how personal data has collected, stored and used, including the actions to be taken in case of personal data breach incident. According to the policy, The Data Protection Officer (DPO) is responsible for integrating data breach issues into enterprise risk management, assessing the impact and raising employee awareness on the personal data protection issues. Moreover, in order to comply with the Act, BJC has established a customer data collection process that emphasizes customer data storage, authorized use of personal data, and data protection methods. The company has developed a process to inform customers about the purpose and use of personal information via a privacy notice on the company website and a consent letter. As a result of efficient data management, there has been no substantiated reports issued by BJC over consumer privacy violations. As a result of efficient data management, there has been no complaint on customer privacy, no substantiated reports issued by BJC over consumer privacy violations, and 7% of customers’ data has been used for secondary purposes in 2022. The company has developed a process to inform customers about the purpose and use of personal information via a privacy notice on the company website and a consent letter.
In addition, at Big C, the company uses a Point of Sale system where customers are asked for their consent prior to joining the Big C Big Card membership program. Once their consent is given, the information is stored in a PDPA Management System database which operated by MIS department. The PDPA Management System allows responsible personnel to request for personal data, remove consent to store, share or use data as well as delete their data. Personal information is protected through the process of role permission, user authorization and censoring personal data (e.g. personal identification number). A CRM Maxar (Terabit) system is used for monitoring percentage of users whose customer data is used for secondary purposes.
Cybersecurity Training
To elevate employee's knowledge, skills and abilities related to cybersecurity, BJC provide e-learning course for all employees to access through the centralized mobile application. The online training course has been integrated into all employee's compulsory orientation training under the "IT Security Awareness" section. All employees must complete a post-test to evaluate the effectiveness of the training session. Moreover, BJC regularly distributes newsletters related to security tips and IT best practices and warnings reminders via many platform such as E-mail and mobile application to employees for ensuring that they have greater knowledge and comprehension of cyber threats.
Integrated Cloud Computing Platform to improve infrastructure
BJC has implemented Cloud computing platform as an all-in-one solution to manage, process, store, and protect customer data from identity theft by using a single platform via drive and google vault. The customer data has been quickly retrieved or access the most update information with patching update.
BJC has implemented Cloud computing platform as an all-in-one solution to manage, process, store, and protect customer data from identity theft by using a single platform via drive and google vault. The customer data has been quickly retrieved or access the most update information with patching update. The platform reduce data damage caused by document storage in international standard with limited authorized access. In 2020, this system provides 100% coverage of online shopping channels for effective protection against cyberattacks, and BJC is committed to continuous improve protection system to keep up with changing technology.

Established Cloud CND into IT system
In order to have an adaptation to technological transformation, Cloud CND has been implemented to provide more effective cyber security by securing Internet properties against denial-of-service attacks (DDoS), customer data breaches, and abusive bots with Advanced DDoS Mitigation as a shield to multiple networks.
In order to have an adaptation to technological transformation, Cloud CND has been implemented to provide more effective cyber security by securing Internet properties against denial-of-service attacks (DDoS), customer data breaches, and abusive bots with Advanced DDoS Mitigation as a shield to multiple networks. The system has also increased the speed of accessing and the efficiency of loading Big C online shopping more than 29% in 2020. From the information, the result shown that the systems has positive affect to BJC businesses in terms of cybersecurity and enhance work efficiency of online websites which improve customer satisfaction as well.
